Introduction
World population is the number of humans living on Earth. This unit describes how the world’s population has grown over the centuries, where people live , the problems that countries have and the dangers of overpopulation.
The world population clock shows the world’s current population.
Today, more than 8 billion people live on our Earth. Each year, the world’s population grows by about 80 million. If it continues to grow at such a rate the world’s population will reach 9 billion by the year 2035.
World Population From the Beginnings to the Present
Human beings have been living on Earth for over a million years, but for a long time there were not very many of them. The world’s population was never higher than 10 million. People died quickly because they didn’t have enough food to eat. Early inhabitants were mostly hunters and fishers. Some of them gathered berries from wild plants. After people started growing crops and raising animals they had more food and lived longer.
When Jesus Christ was born about 2,000 years ago about 300 million people inhabited the Earth. During the next 1500 years the population of the world grew very slowly. Many people died of illnesses and plagues . The Black Death , which sailors brought to Europe from Asia, killed about a third of the European population in the Middle Ages.
The Industrial Revolution , which began in the middle of the 18th century, started a period of rapid population growth , especially in Europe. Farmers were able to grow more and more food because they had machines to work with. New kinds of medicine helped to fight off many diseases that had killed millions of people in the centuries before. Humans also lived longer because they had cleaner drinking water.
Birth rates started to go up because families had many children. More babies than ever before survived the first few years of childhood . The one billion mark was reached in the early 1800s. In the next one hundred years the population doubled to 2 billion, and in 1960 there were 3 billion people living on Earth.
The second half of the 20th century brought along some change :
- In Europe , North America, Japan and Australia the birth rate dropped because families wanted to have fewer children. Population growth in these areas slowed down .
- In the developing countries of Asia and Africa birth rates stayed high and better medical help in these regions lowered the death rates. That is why these countries are growing very rapidly .
- Countries with a fast growing population
These pyramids show a strong base and a very narrow top. Birth rates are high and there many children and young people. People also die earlier than in Europe or North America. - Countries with zero growth
The number of births reached its peak during the baby boom of the 1950s and 60s. Since then the birth rate has been constant. - Counties with declining population
Many European countries have such a population structure. Families are having fewer children and the death rate is sometimes higher than the birth rate. The baby boomers of the past century are getting older and older, which leads to many pensioners. These countries can only grow if they have enough immigrants who come to live and work there. - more and better jobs
- better hospitals and health care
- better living standards
- cities are social and financial centres
- better education—schools and universities
- too many people in the countryside
- low income
- not enough raw materials (water, wood etc..)
- the quality of farming land is getting worse
- Central and South America to North America
- Eastern Europe and the countries of the former Soviet Union to Western Europe
- Africa and Asia to Europe
- the Middle East to Europe
- More and more people need room to live. They are taking away the living areas of animals and plants.
- Cities have problems making enough drinking water for thousands of people who want to start a new life there every year.
- Population in rural areas is growing too. People need more food and have to grow more crops on the same land. This means that the quality of the soil is getting worse and worse.
- More and more trees are being destroyed, especially in tropical regions. More carbon dioxide, which is usually taken up by trees, is now set free into the atmosphere. This leads to global warming.
In the last 30 years the world’s population has doubled. The fastest growing regions are Africa with a growth rate of 2.5 %, and Latin America with a growth rate of 0.7% per year. In Europe the population is decreasing by about 0.3 %. On average, the world’s population is growing at a rate of 1.1 % per year.
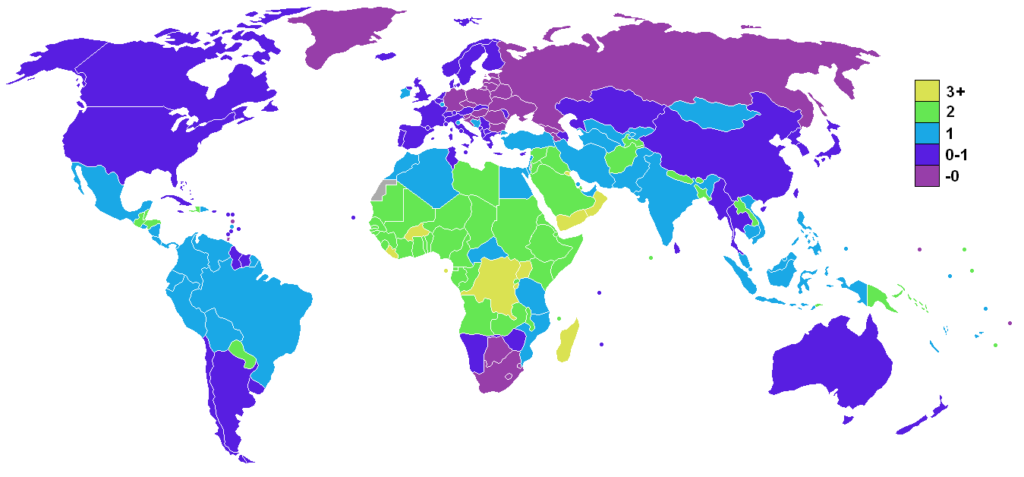
World population growth in percent
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Population_growth_rate_world.png ,
CC BY-SA 3.0 DEED
The 10 Most Populous Countries (2024)
| Rank | Country | Population in millions |
| 1 | India | 1 428 |
| 2 | China | 1 425 |
| 3 | USA | 339 |
| 4 | Indonesia | 277 |
| 5 | Pakistan | 240 |
| 6 | Nigeria | 223 |
| 7 | Brazil | 216 |
| 8 | Bangladesh | 172 |
| 9 | Russia | 144 |
| 10 | Mexico | 128 |
Continents’ share of world population – own work
Population Density
Population density tells us how many people live on one square kilometre of land. The world’s population is not spread evenly over the continents. Asia and Europe are the most densely populated continents. Many other areas of the world , like deserts, polar regions or high mountains are very sparsely ,or not at all populated .
About 90% of the Earth’s people live on only 10% of the land. Most of them live north of the equator because two thirds of the Earth’s landmasses are there.
Many people also live near coastal regions . In China, for example, 80% of the country’s inhabitants live in the eastern part of the country near the coast. In South America, most people live in the big cities, which all lie in coastal areas.
There are many reasons why people live in certain places. Areas with moderate temperatures and enough rainfall are densely populated, because people find good farming conditions there. Raw materials also attract groups of people. North-western Germany and parts of England are densely populated because coal is mined there. Economic reasons also play an important role in choosing where to live. People go to places where they can find jobs and where the economy is strong.
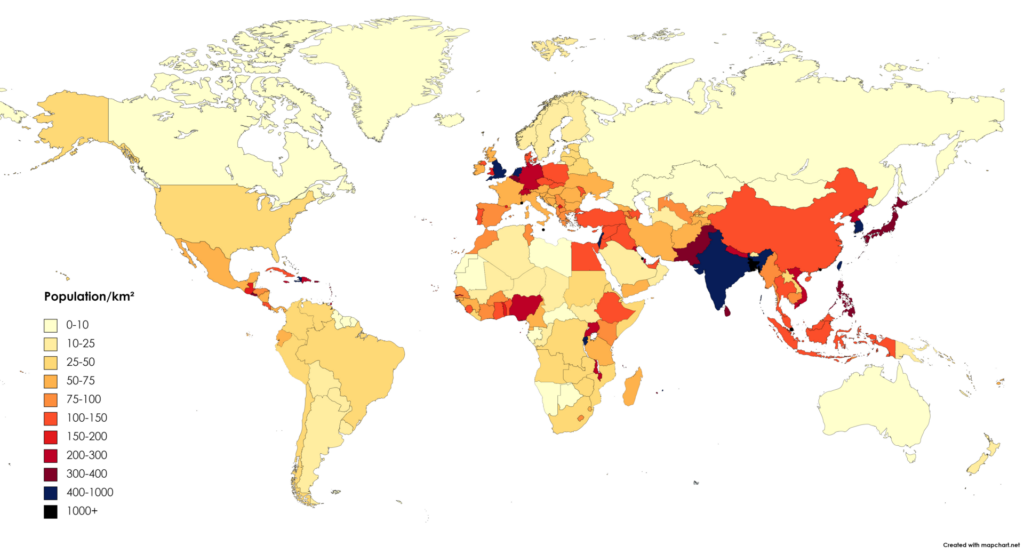
World Population Density
Image: English English is Correct, CC0,
via Wikimedia Commons
Population Pyramids
Population pyramids tell us how many people there are in a certain age group as well as the number of men and women in these groups.
There are three different types of pyramids:
Such pyramids also can tell governments which problems they will be facing in the future. Countries , in which more than half of the population is under 18, will need more and more schools and later on enough jobs to give all citizens work.
Countries with a declining population have a high number of older people. They don’t have enough young workers to pay the pension for these people when they retire. Such countries need more hospitals and old people’s homes to care for their elderly citizens.
Almost all pyramids show that, although more boys are born than girls, there are more older women than men. This is, partly, because women live longer than men—3 to 5 years on average.
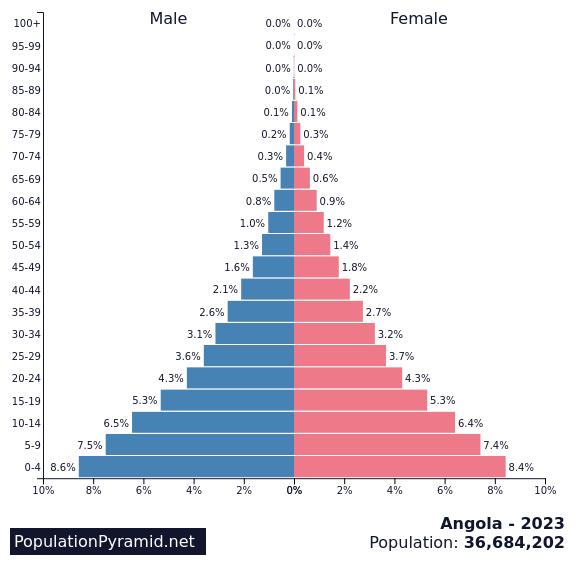
Angola – Fast growing population
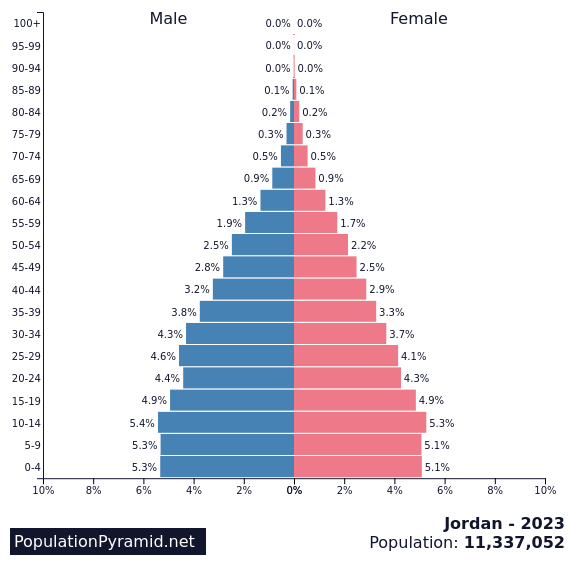
Jordan – Zero growth
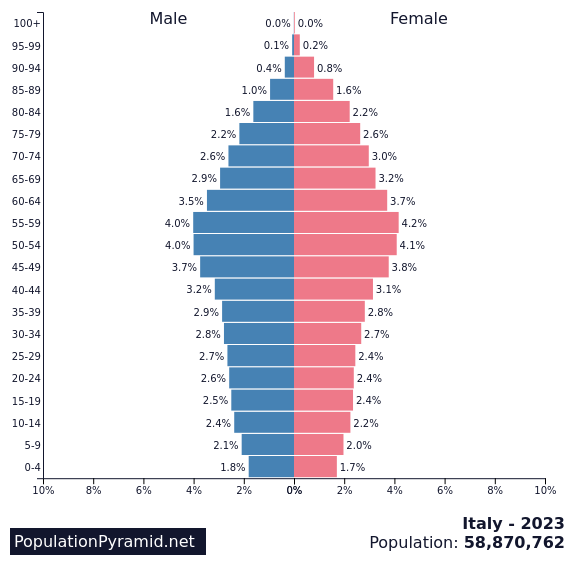
Italy – Declining population
Source : PopulationPyramid.net Licence: CC BY 3.0 IGO
City Population
Up to the Industrial Revolution people all over the world lived mainly in the countryside. In 1800, only 3 % of the world’s population lived in cities. In 1900 only 12 cities had more than 1 million people.
Today, about half of the world’s population lives in urban areas. There are over 500 cities with more than a million people. In developed countries, up to 70 % or more live in larger cities, whereas in poorer countries this rate is below 40 %.
During the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century cities grew fast, especially in Europe and North America, because new industries were created there and people found many jobs . Later on cities grew more slowly because they became overcrowded and diseases could spread faster. Today death rates in cites are low because they have better doctors and more hospitals.
In industrialized countries the growth of cities has stopped. New York and London grew very quickly during the 1800s and early 1900s, but since then their growth has slowed down.
African and Asian cities like Lagos, Bombay or Calcutta are growing rapidly and this will probably continue during the next years. About 40 cities around the world have a population of over 5 million . They are called megacities . 80% of them are in poorer countries.
People go to the cities for many reasons. The table shows you what pulls them to the cities and what pushes them away from the countryside.
Pull Factors
Push Factors
The largest cities in the world (2023) – own work
China’s One Child Policy
In 1979 the Chinese government started its “one child” policy because the population of the country was growing too fast. A married couple was only allowed to have one child. If families followed this government plan they would get free education, health care and money for their only child. However, families that had two or more children were punished. They had to pay for everything themselves and got no help from the government. They even had to pay more tax.
To help control population growth, China allowed women to have free abortions and gave them birth control pills for free.
The government’s plan also caused many problems for China. Parents often wanted to have a boy instead of a girl in order to carry on the family name. As a result female babies were often left on the streets by their mothers and some were even killed. 90% of unborn babies that are aborted are female.
In the last 40 years China’s population growth has slowed down. Without the one-child policy there would probably be about 300 million more people living in China today. The law worked mostly in cities, where the government had more control over the people. In the countryside where a lot of poor farmers and minorities lived , the laws were not so strict. People were not punished for having two or more children
China ended its one-child policy in 2016. The government started allowing families to have two children. In 2021 they allowed familes three children.
Migration
Migration means leaving your home country and living or working somewhere else. Some countries, like the USA, have a population that is made up mainly of immigrants or their descendants who have arrived there in the past 200 years.
Today, about 150 million people live outside their native countries. The biggest movements of people are from
People leave their home countries for many reasons. Sometimes they think they can get better jobs and more money in richer countries. Sometimes they leave their own country for political reasons or because of their religion.
During the course of history people have left their homes because of unemployment, wars in their country or because of a famine. Thousands of Irish men and women left the island in the middle of the 19th century because there was a potato crisis and many of them didn’t have enough to eat.
The Balkan wars in the 1990s left millions of people homeless. They became refugees and went to neighboring countries to the north and west. Conflicts in the Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan brought over 1.5 million people to Western Europe in 2015 alone.
Some countries depend on immigrants to keep their economy running or because they have low birth rates and need foreigners to work. Today, governments in many countries face illegal immigration. Especially the USA and countries in Western Europe are sending back more and more people to their home countries.
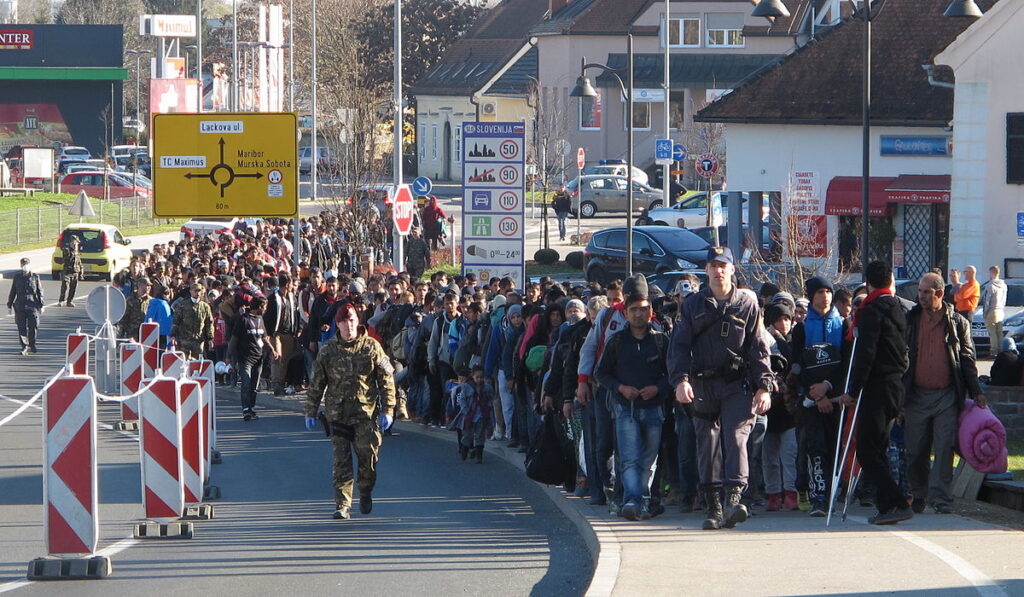

Refugees at the Slovenian – Austrian border in 2015
Image:Borut Podgoršek, MORS, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Status of Women
The situation of women in our world today is very important. There are many differences between richer and poorer countries.
In industrialized countries birth rates have fallen since the 1960s. One reason is that more and more women have jobs and go to work. They do not want to stay at home any longer and have fewer babies.
In developing countries the situation of women is different. Many of them are at home, do the household chores and care for their children.
Helping women in the Third World is very important and can slow down the population explosion. One of the key factors is education. Women who go to school and maybe later on study at a university have higher chances of getting a job. They don’t marry so early and start having children at a later age.
Such women also know more about birth control and can plan the number of children they want to have.
Educated women also know more about health care. Young girls who have sex at an early age risk getting AIDS and passing it on to their babies when they are pregnant. More than half of the 40 million people living with AIDS today are women. In Africa, more than 75 % of all AIDS victims are young women between 15 and 24.
Number of births per 1,000 people
Image: Korakys, CC BY-SA 4.0,
via Wikimedia Commons
Old Age
Developed countries all over the world have the same problem. Their birth rates are falling and people are getting older. Medical and health care is getting better all the time. We call this an ageing society.
In industrialized countries life expectancy is getting higher and higher. In most European countries women reach an average of over 80 years and men live up to about 78.
We need more and more people who care for the elderly. This means building more old people’s homes and other care units.
The government must spend more money on pensions. This won’t work if we don’t have enough young people who have jobs and pay taxes. More and more people have to work up to 65 and longer. They take away jobs that young adults need.
An older labor force means that we are not as flexible and productive as countries that have young workers.
Dangers of Overpopulation
The world’s population is growing by almost 80 million people every year. We will be facing many problems in the future:
Environmental Problems
Poverty
Population growth is highest in developing countries. Young people have to care for their parents and grandparents, so they have less money to buy the things that they need. They stay poor.
Africa is the fastest-growing continent on earth. But its people are getting poorer and poorer. Every third person in Africa doesn’t have enough to eat. The average African family has about 5 children.
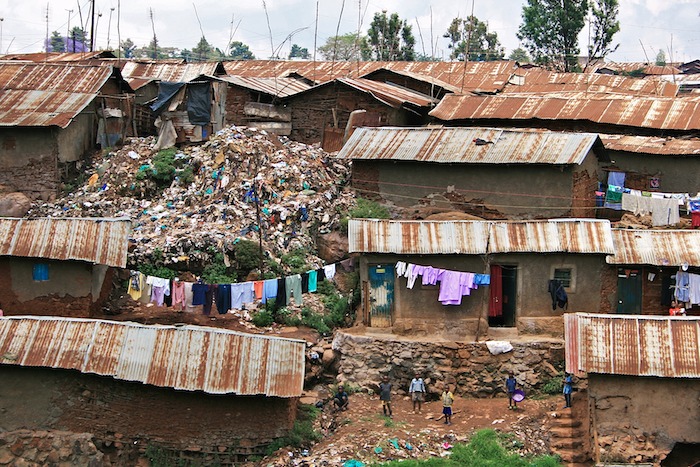

Houses in a slum in Nairobi, Kenya
Image:Colin Crowley, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Food and Water
The “ Green Revolution” of the 1960s and 70s has given farmers better methods and tools to grow crops and food. But ,still, they cannot produce enough to feed the growing population. Food will get expensive for these countries because some of them have to buy it from industrial countries. Many people die of starvation and millions more will die in the future. In addition , about 400 million people all over the world live in places where there is not enough drinking water.
Unemployment
Many Third World countries have a high number of children or young people. Unemployment will be going up over the next decades, because the governments cannot create enough jobs to give work to its younger generation. Young people who can’t find any work sometimes try to get money by stealing, dealing with drugs or doing other illegal things. This might lead to social unrest in such countries.
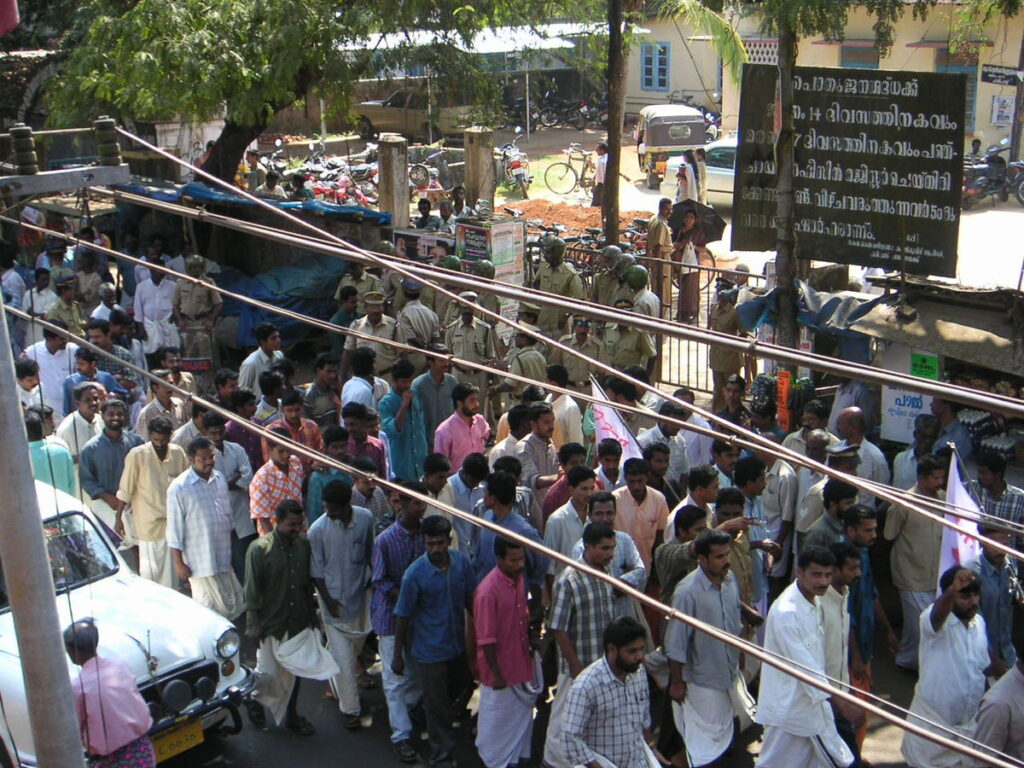

Demonstration against unemployment in southern India
Image:No machine-readable author provided. Soman assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0,
via Wikimedia Commons