Ancient Greece was the first civilization in Europe. It developed around the eastern part of the Mediterranean Sea . Many powerful cities , great thinkers and scientists emerged in ancient Greece. It was also the birthplace of democracy.
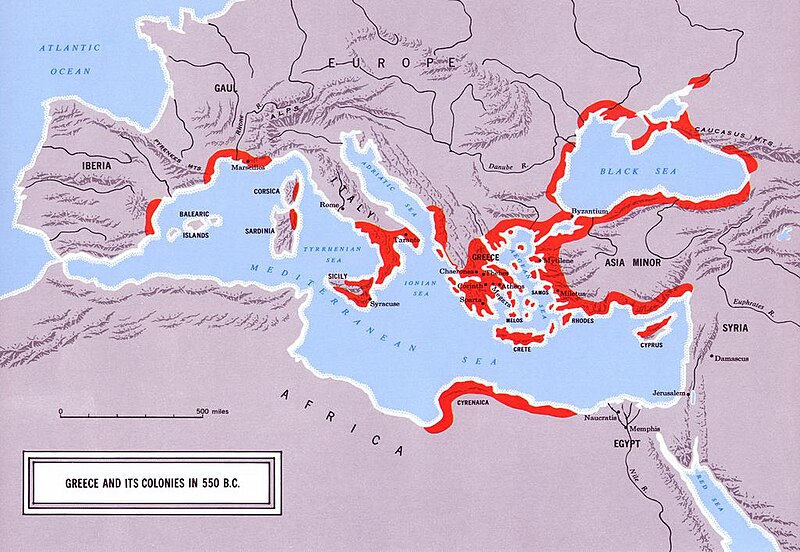
Greece and its colonies around 500 B.C.
Image:Thrasis, CC BY-SA 3.0,
via Wikimedia Commons
History of Ancient Greece
Aegean Civilizations
As Greek city-states became weaker Macedonia, a kingdom to the north of Greece, grew stronger and stronger. After King Philipp II had conquered all of Greece his son, Alexander, came to power in 336 BC. He set out to conquer Persia and got as far east as India . Alexander the Great spread Greek ideas and the Greek way of life throughout western Asia and the Middle East.
City States
After 1000 B.C. Dorians and Ionians, who settled in the eastern part of Greece started to build large cities. These cities had their own governments , their own armies and were independent .
The two most powerful city states were Sparta and Athens. Sparta was the strongest and most powerful city state with many soldiers and a huge army. It was only interested in fighting wars. Sparta united surrounding villages and sent armies to conquer its neighbours and bring back slaves .
Athens, on the other side, concentrated on trade , science and other fields. It was the first city to form a democratic government.
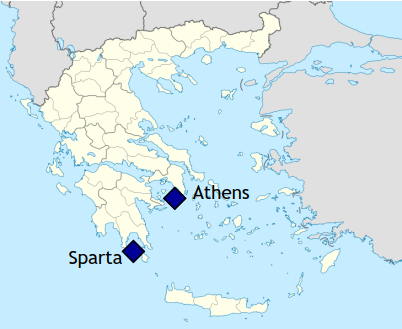
Sparta and Athens – the two most powerful city states
Persian Wars
At about 500 B.C. the Persian empire under Darius I invaded many Greek cities on the Asian coast. By 490 BC the Persians attacked the Greek mainland . Greek armies under Spartan leadership fought back and defeated the Persians.
Peloponnesian War
Under the rule of Pericles Athens had become the most powerful city-state and controlled most of the eastern part of Greece. Pericles wanted to make Athens a beautiful city with many temples. Art , philosophy and general knowledge became important. Sparta thought that Athens would become too powerful. In 431 BC it began a war against Athens.
In 430 BC a plague broke out in Athens and killed a third of its population. After becoming weaker and weaker it finally surrendered to the Spartan army.
Macedonian Rule
As Greek city-states became weaker Macedonia, a kingdom to the north of Greece, grew stronger and stronger. After King Philipp II had conquered all of Greece his son, Alexander, came to power in 336 BC. He set out to conquer Persia and got as far east as India . Alexander the Great spread Greek ideas and the Greek way of life throughout western Asia and the Middle East.
Alexander did not name a successor to his empire . After his death many generals fought for power and his empire broke up into many kingdoms .
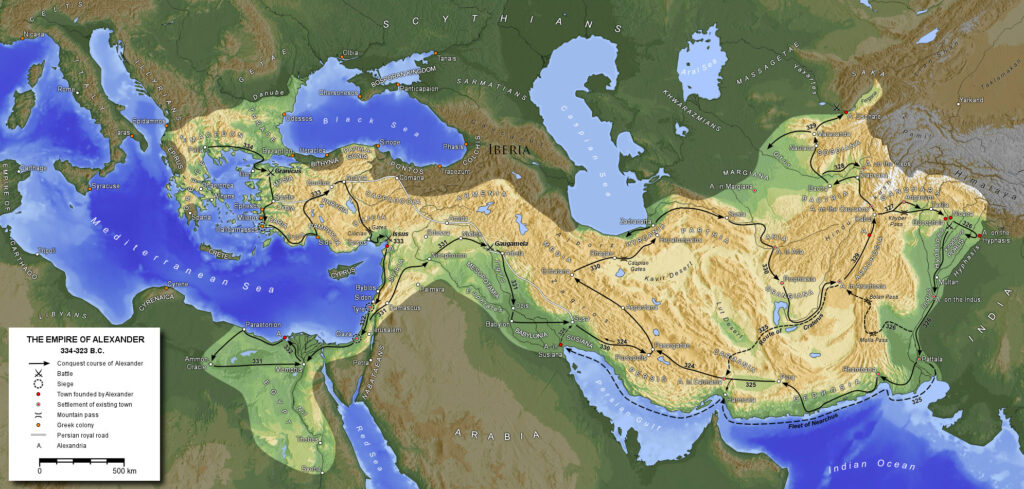
Empire of Alexander the Great
Image : Generic Mapping Tools, CC BY-SA 3.0,
via Wikimedia Commons
Roman Rule
In 140 BC Rome took over Greece and the city states. They stayed under Roman rule until 395 AD and then became part of the Byzantine empire .
Daily Life in Ancient Greece
Men were the heads of most Greek families. Richer families had slaves who were commanded by the wives. They had to look after the children and do the household work.
Most Greek families arranged weddings for their children. Women usually married at an early age, men much later.
In ancient Greece society was made up of citizens and non-citizens. Citizens were free men and noblemen. They owned land and took part in government . Non-citizens were women, slaves and serfs .
Only citizens received education. Teachers in Athens taught general subjects like music, writing, mathematics and reading. They also concentrated on physical exercise like running, jumping and wrestling . Education in Sparta was different. Boys were sent to military schools so that they could become good soldiers .
Greek people ate food made of grains , mostly wheat or barley . Bread was the main type of food. They ate fish and eggs for protein and consumed vegetables and fruit .
Greek men and women wore garments made of linen or wool that hung down to their knees. They also wore a belt around their waist . A woman’s garment usually covered her whole legs down to her ankles .
Houses were small in ancient Greece. Because of the mild climate many things were kept outside the house. Poor families lived in houses made of dried bricks and floors made of dried and hard mud . Wealthy families had stone floors and separate rooms for cooking, eating and sleeping.

Food preparation in ancient Greece
Image: Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0,
via Wikimedia Commons
Woman’s clothes
Image: Creazilla – Open Source
Philosophy, Science and Arts
Ancient Greece became famous for its great thinkers and philosophers. Socrates, Plato and Aristotle were great men who looked for logical explanations of everyday things. Many people in Greece, however, did not believe in what philosophers had to say. In 399 B.C. Socrates was sentenced to death because of his teachings and because he did not believe in Greek gods.
Famous playwrights and poets wrote works that are still performed in theatres today. Architects designed beautiful buildings.
Scientists explored medicine, physics , biology and mathematics. They observed nature and also carried out experiments.

Bust of Socrates
Image: Photograph by Greg O’Beirne. Cropped by User:Tomisti, CC BY-SA 3.0,
via Wikimedia Commons
Religion
People in ancient Greece believed in many gods. On one hand gods and goddesses were like normal people who showed feelings but on the other hand they possessed abilities that humans didn’t. They could foretell the future and live forever.
Normal people thought that gods and goddesses watched them and observed what they did in everyday life. They spoke to the people through oracles, holy places where priests had contact with gods. The most important oracle was at Delphi.
Zeus was the most important god. He and his wife Hera lived on Mount Olympus. Other gods and goddesses included
- Aphrodite, the goddess of love
- Eros, god of love
- Apollo, the god of light
- Ares, the god of war
- Athena, the goddess of wisdom
Democracy and Politics
The idea of democracy, which means government by the people, came from ancient Greece. Athens was the first city to set up a democratic government.
All free men were members who passed laws and were also allowed to serve on a jury .
Of the 30,000 citizens in Athens 500 were chosen each year to help run the city. They received a small amount of money because they could not continue their normal work.